What Is 30 Million Euros To RMB And Why Does It Matter?
Navigating the complexities of currency exchange can be daunting. At euro2.net, we simplify this process, offering real-time data and expert analysis. Understanding the conversion of 30 Million Euros To Rmb is crucial for investors, businesses, and travelers alike, and this article explores the intricacies of this conversion, the factors influencing it, and how euro2.net can assist you in making informed decisions. We’ll delve into currency diversification and exchange rate dynamics, providing actionable insights for financial success.
1. Understanding the Euro (EUR) and the Renminbi (RMB)
What are the euro and the renminbi, and what factors influence their values?
The euro (EUR) is the official currency of the Eurozone, a monetary union of 20 member states of the European Union. It is the second most widely held currency in the world and plays a significant role in international trade and finance. According to the European Central Bank (ECB), the euro’s stability is maintained through monetary policy decisions that aim to control inflation and promote economic growth.
The renminbi (RMB), also known as the Chinese yuan (CNY), is the official currency of the People’s Republic of China. As China’s economic influence grows, the RMB is increasingly used in global trade and investment. The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) manages the RMB’s exchange rate through a managed floating exchange rate system, which allows the currency to fluctuate within a specified band against a basket of other currencies.
Several factors can influence the values of the EUR and RMB:
- Economic Performance: Economic growth, inflation rates, and employment figures in the Eurozone and China significantly impact their respective currencies. Higher growth rates typically lead to stronger currencies.
- Monetary Policy: Decisions made by the ECB and PBOC regarding interest rates and quantitative easing can influence currency values. Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency.
- Geopolitical Events: Political instability, trade tensions, and international relations can create volatility in currency markets. For example, trade disputes between the U.S. and China have historically affected the RMB’s value.
- Market Sentiment: Investor confidence and speculative trading can also drive currency movements. Positive sentiment towards an economy often leads to increased investment and currency appreciation.
- Government Policies: Government interventions, such as currency controls and fiscal policies, can directly impact currency values. China’s capital controls, for example, influence the RMB’s exchange rate.
Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone looking to convert EUR to RMB or vice versa, especially when dealing with large sums like 30 million euros. Real-time data and expert analysis, like those available on euro2.net, can help you navigate these complexities and make informed decisions.
2. Current EUR/RMB Exchange Rate Dynamics
What are the current trends in the EUR/RMB exchange rate, and what factors drive these trends?
The EUR/RMB exchange rate is influenced by various global economic factors. As of November 2024, the exchange rate has shown notable volatility due to shifts in economic policies and market sentiment.
Recent Trends:
- Fluctuations: The EUR/RMB exchange rate has experienced fluctuations influenced by economic data releases from both the Eurozone and China.
- Impact of Economic Data: Positive economic indicators from the Eurozone, such as strong GDP growth or declining unemployment rates, tend to strengthen the euro against the RMB. Conversely, positive data from China can strengthen the RMB.
- Policy Changes: Monetary policy decisions by the European Central Bank (ECB) and the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) play a crucial role. Interest rate adjustments, quantitative easing, and other policy changes can significantly impact the exchange rate.
Key Drivers:
- Interest Rate Differentials: Differences in interest rates between the Eurozone and China attract or deter foreign investment, affecting currency demand.
- Trade Balance: The trade balance between the Eurozone and China influences currency flows. A trade surplus in favor of the Eurozone can increase demand for the euro, while a surplus for China can boost the RMB.
- Geopolitical Events: Events like trade negotiations, political instability, and international relations impact investor sentiment and currency values.
- Market Sentiment: Overall market sentiment and investor risk appetite can drive currency movements. Positive sentiment towards either economy can lead to increased investment and currency appreciation.
- Global Economic Conditions: Broader global economic conditions, such as the strength of the U.S. dollar and global trade patterns, also play a role in shaping the EUR/RMB exchange rate.
Staying informed about these trends and drivers is essential for anyone dealing with EUR/RMB conversions. Platforms like euro2.net provide up-to-date data and expert analysis to help you make informed decisions.
3. Converting 30 Million Euros to RMB: A Detailed Calculation
How do you calculate the conversion of 30 million euros to RMB, and what are the potential costs involved?
Converting 30 million euros to RMB involves a straightforward calculation using the current exchange rate. However, it’s crucial to consider all potential costs to ensure an accurate assessment.
Calculation:
-
Find the Current Exchange Rate: Obtain the latest EUR/RMB exchange rate from a reliable source like euro2.net. For example, if the exchange rate is 1 EUR = 7.8 RMB.
-
Multiply the Amount: Multiply the amount you want to convert (30 million euros) by the exchange rate.
- 30,000,000 EUR * 7.8 RMB/EUR = 234,000,000 RMB
Potential Costs:
- Exchange Rate Fluctuations: Exchange rates can change rapidly, so the rate used for the calculation might differ slightly from the actual rate at the time of the transaction.
- Transaction Fees: Banks and currency exchange services often charge fees for converting currency. These fees can be a percentage of the total amount or a fixed fee.
- Commission: Some services charge a commission on top of the exchange rate.
- Bank Charges: Banks may charge additional fees for international transfers, including receiving fees and intermediary bank fees.
- Spread: The spread is the difference between the buying and selling price of a currency. Currency exchange services profit from this difference, so it’s an implicit cost to consider.
- Taxes: Depending on the jurisdiction and the purpose of the transaction, taxes may apply to currency conversions.
Example of Potential Costs:
Let’s assume the following:
- Exchange rate: 1 EUR = 7.8 RMB
- Transaction fee: 0.1%
- Commission: 0.05%
- Bank charges: 50 EUR
- Base Conversion: 30,000,000 EUR * 7.8 RMB/EUR = 234,000,000 RMB
- Transaction Fee: 30,000,000 EUR * 0.001 = 30,000 EUR
- Commission: 30,000,000 EUR * 0.0005 = 15,000 EUR
- Bank Charges: 50 EUR
Total Costs: 30,000 EUR + 15,000 EUR + 50 EUR = 45,050 EUR
Net Conversion: 30,000,000 EUR – 45,050 EUR = 29,954,950 EUR
29,954,950 EUR * 7.8 RMB/EUR = 233,648,610 RMB
This example shows that the costs can significantly impact the final amount received. Always compare services and rates to minimize these costs. Euro2.net can help you find the best exchange rates and understand potential fees.
4. Factors Influencing the EUR/RMB Exchange Rate
What are the macroeconomic factors, geopolitical events, and policy changes that affect the EUR/RMB exchange rate?
The EUR/RMB exchange rate is subject to a complex interplay of macroeconomic factors, geopolitical events, and policy changes. Understanding these influences is vital for anyone involved in currency exchange and international finance.
Macroeconomic Factors:
- Economic Growth: The relative economic growth rates of the Eurozone and China significantly impact the EUR/RMB exchange rate. Higher growth in China tends to strengthen the RMB, while stronger growth in the Eurozone boosts the euro.
- Inflation Rates: Inflation rates in both regions influence the purchasing power of their currencies. Higher inflation can weaken a currency, making its goods and services more expensive relative to those of other countries.
- Interest Rates: Interest rate policies set by the European Central Bank (ECB) and the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) affect capital flows. Higher interest rates typically attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency and causing it to appreciate.
- Unemployment Rates: Unemployment levels reflect the health of an economy. Lower unemployment rates often indicate a stronger economy, which can lead to currency appreciation.
- Trade Balance: The balance of trade between the Eurozone and China influences currency demand. A trade surplus increases demand for the currency of the exporting country, leading to its appreciation.
Geopolitical Events:
- Trade Relations: Trade agreements, disputes, and tariffs between the Eurozone and China can significantly impact the exchange rate. For example, trade wars or the imposition of tariffs can create uncertainty and volatility.
- Political Stability: Political stability in both regions is crucial. Political unrest or uncertainty can deter investment and weaken a currency.
- International Relations: Broader international relations and geopolitical tensions can also affect the exchange rate. Events such as sanctions, diplomatic disputes, or conflicts can create market volatility.
Policy Changes:
- Monetary Policy: Changes in monetary policy by the ECB and PBOC, such as quantitative easing or tightening, directly impact currency values.
- Fiscal Policy: Government spending and taxation policies can influence economic growth and inflation, thereby affecting currency values.
- Currency Controls: China’s capital controls and management of the RMB’s exchange rate play a significant role. Policy changes regarding these controls can lead to significant currency movements.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in financial regulations can impact investment flows and currency demand.
- Exchange Rate Policies: Any adjustments to the exchange rate regime or interventions by central banks to manage currency values can directly affect the EUR/RMB exchange rate.
Keeping abreast of these factors requires continuous monitoring and analysis. Euro2.net provides up-to-date information and expert insights to help you understand these influences and make informed decisions about currency exchange.
5. Strategies for Managing EUR/RMB Exchange Rate Risk
What strategies can businesses and investors use to manage the risks associated with EUR/RMB exchange rate fluctuations?
Managing EUR/RMB exchange rate risk is crucial for businesses and investors engaged in transactions between the Eurozone and China. Several strategies can help mitigate potential losses due to currency fluctuations.
1. Hedging:
- Forward Contracts: Enter into a forward contract with a bank or financial institution to lock in a specific exchange rate for a future transaction. This eliminates the uncertainty of future rate fluctuations.
- Currency Options: Purchase currency options that give you the right, but not the obligation, to exchange currency at a specific rate on a future date. This provides flexibility while protecting against adverse movements.
- Currency Swaps: Use currency swaps to exchange principal and interest payments on debt denominated in different currencies. This can help manage long-term currency exposure.
2. Natural Hedging:
- Matching Revenues and Expenses: Try to match revenues and expenses in the same currency. For example, if you have expenses in RMB, try to generate revenue in RMB as well.
- Diversifying Markets: Diversify your markets to reduce reliance on a single currency. This can help cushion the impact of adverse currency movements.
3. Pricing Strategies:
- Currency Adjustment Clauses: Include currency adjustment clauses in contracts that allow you to adjust prices based on exchange rate fluctuations.
- Pricing in Local Currency: Consider pricing your products or services in the local currency to avoid exchange rate risk for your customers.
4. Financial Instruments:
- Currency ETFs: Invest in currency exchange-traded funds (ETFs) to gain exposure to currency movements without directly trading currencies.
- Money Market Accounts: Utilize money market accounts denominated in different currencies to manage short-term currency exposure.
5. Monitoring and Analysis:
- Stay Informed: Continuously monitor exchange rates and economic news to anticipate potential movements. Use resources like euro2.net to stay updated.
- Expert Advice: Seek advice from financial professionals who specialize in currency risk management.
6. Centralized Treasury Management:
- Consolidated Approach: Implement a centralized treasury management system to manage currency risk across the entire organization. This allows for a more coordinated and effective approach.
Example:
A Eurozone-based company exporting goods to China can use a forward contract to lock in an exchange rate for their RMB revenues. This ensures they receive a predictable amount in euros, regardless of exchange rate fluctuations.
By implementing these strategies, businesses and investors can effectively manage EUR/RMB exchange rate risk and protect their financial interests.
6. Tax Implications of Converting EUR to RMB
What are the tax considerations when converting EUR to RMB, and how can you ensure compliance?
Converting EUR to RMB can have various tax implications depending on the jurisdiction, the nature of the transaction, and the parties involved. Understanding these tax considerations is crucial for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential penalties.
1. Income Tax:
- Capital Gains Tax: If the conversion results in a profit due to exchange rate fluctuations, this may be subject to capital gains tax. The specific rules vary by country. For example, in the U.S., gains from currency transactions are generally treated as ordinary income or short-term capital gains.
- Business Income: For businesses, currency gains or losses may be treated as part of their business income. This income is then subject to corporate tax rates.
2. Value Added Tax (VAT):
- VAT Implications: Currency conversion itself is generally exempt from VAT. However, if the conversion is related to a taxable supply of goods or services, VAT may apply to the underlying transaction.
3. Withholding Tax:
- Cross-Border Payments: When converting EUR to RMB for cross-border payments, withholding tax may apply. This tax is levied on income paid to non-residents and varies depending on tax treaties between countries.
4. Reporting Requirements:
- Thresholds: Many countries have reporting requirements for large currency transactions. For example, in the U.S., financial institutions must report transactions over $10,000 to the IRS.
- Foreign Bank Account Reporting (FBAR): U.S. citizens and residents must report foreign bank accounts with an aggregate value exceeding $10,000 at any time during the calendar year.
- FATCA: The Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) requires foreign financial institutions to report information about accounts held by U.S. taxpayers to the IRS.
5. Transfer Pricing:
- Related Party Transactions: If the EUR to RMB conversion involves related parties (e.g., subsidiaries of the same company), transfer pricing rules may apply. These rules ensure that transactions are conducted at arm’s length to prevent tax avoidance.
6. Tax Treaties:
- Double Taxation: Tax treaties between countries can help avoid double taxation. These treaties often provide rules for determining which country has the right to tax certain types of income.
7. Compliance Tips:
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all currency transactions, including exchange rates, fees, and the purpose of the conversion.
- Professional Advice: Consult with a tax advisor who specializes in international transactions.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of changes in tax laws and regulations in both the Eurozone and China.
- Use Reputable Services: Use reputable currency conversion services that comply with all applicable tax laws and reporting requirements.
Example:
A U.S. company converts EUR to RMB to pay a Chinese supplier. The company must report the transaction to the IRS if it exceeds $10,000 and may be subject to withholding tax on the payment to the supplier.
By understanding these tax implications and taking appropriate compliance measures, individuals and businesses can ensure they meet their tax obligations when converting EUR to RMB.
7. Choosing the Right Currency Exchange Service
How do you select the best currency exchange service for converting EUR to RMB, considering factors like fees, exchange rates, and security?
Choosing the right currency exchange service is crucial for ensuring you get the best value and security when converting EUR to RMB. Several factors should be considered to make an informed decision.
1. Exchange Rates:
- Compare Rates: Always compare exchange rates from multiple providers. Exchange rates can vary significantly, and even small differences can add up when converting large sums like 30 million euros.
- Real-Time Rates: Look for services that offer real-time exchange rates. This ensures you get the most up-to-date information.
- Transparency: Choose providers that are transparent about their exchange rates and how they are determined.
2. Fees and Commissions:
- Transaction Fees: Check for transaction fees, which can be a fixed amount or a percentage of the transaction.
- Commissions: Some services charge a commission on top of the exchange rate. Be aware of this additional cost.
- Hidden Fees: Watch out for hidden fees, such as receiving fees or intermediary bank fees. Read the fine print carefully.
3. Security:
- Regulation: Ensure the service is regulated by a reputable financial authority. Regulation provides oversight and protection for consumers.
- Encryption: Look for services that use strong encryption to protect your personal and financial information.
- Insurance: Check if the service offers insurance to cover potential losses due to fraud or theft.
4. Convenience:
- Online Platforms: Consider online platforms that offer 24/7 access and convenience.
- Physical Locations: If you prefer face-to-face service, choose a provider with convenient physical locations.
- Transfer Options: Look for services that offer various transfer options, such as bank transfers, wire transfers, and cash pickups.
5. Customer Service:
- Availability: Choose a service with responsive and helpful customer service.
- Reviews: Read customer reviews to get an idea of the service’s reputation.
- Support Channels: Check if the service offers multiple support channels, such as phone, email, and live chat.
6. Transfer Limits:
- Transaction Limits: Be aware of any transaction limits. Some services may have restrictions on the amount you can convert or transfer.
- Reporting Requirements: Ensure the service complies with reporting requirements for large transactions.
7. Speed:
- Transfer Times: Check the transfer times. Some services offer faster transfers than others.
- Cut-off Times: Be aware of cut-off times for same-day transfers.
Examples of Currency Exchange Services:
- Banks: Traditional banks offer currency exchange services but may have higher fees and less favorable exchange rates.
- Online Platforms: Online platforms like Wise (formerly TransferWise), Remitly, and OFX offer competitive rates and lower fees.
- Currency Exchange Brokers: Currency exchange brokers specialize in currency conversions and can offer personalized service and better rates for large transactions.
How to Compare Services:
- Get Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple services for the amount you want to convert.
- Calculate Total Cost: Calculate the total cost, including fees, commissions, and any other charges.
- Compare Net Amounts: Compare the net amount you will receive in RMB after all costs are deducted.
- Check Security Measures: Verify the security measures and regulatory compliance of each service.
- Read Reviews: Read customer reviews to get an idea of the service’s reputation.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the right currency exchange service for your needs and ensure a smooth and cost-effective EUR to RMB conversion.
8. Alternative Currencies to Consider
What are alternative currencies that businesses and investors can consider to reduce reliance on the EUR and RMB?
Diversifying currency holdings can reduce risk and provide stability in international transactions. Here are alternative currencies that businesses and investors can consider to reduce reliance on the EUR and RMB:
1. United States Dollar (USD):
- Global Reserve Currency: The USD is the world’s primary reserve currency and is widely used in international trade and finance.
- Liquidity: High liquidity makes it easy to convert and use in transactions.
- Stability: Generally considered a stable currency, although it is subject to fluctuations based on U.S. economic and political factors.
2. Japanese Yen (JPY):
- Safe Haven Currency: The JPY is often considered a safe haven currency during times of global economic uncertainty.
- Low Interest Rates: Japan’s low interest rates can make it attractive for borrowing.
- Strong Economy: Japan has a strong and diversified economy.
3. British Pound (GBP):
- Major Global Currency: The GBP is one of the world’s major currencies and is widely used in international trade.
- Established Financial System: The UK has a well-established financial system and is a major financial center.
- Volatility: Brexit has introduced some volatility to the GBP.
4. Swiss Franc (CHF):
- Safe Haven Currency: The CHF is another safe haven currency due to Switzerland’s political neutrality and stable economy.
- Strong Banking System: Switzerland has a strong and reputable banking system.
- Low Inflation: Switzerland has a history of low inflation.
5. Canadian Dollar (CAD):
- Resource-Based Economy: The CAD is tied to Canada’s resource-based economy, particularly oil.
- Stable Political System: Canada has a stable political system and a well-regulated financial system.
- Close Ties to the U.S.: Canada’s close economic ties to the U.S. can make it a good alternative to the USD.
6. Australian Dollar (AUD):
- Commodity Currency: The AUD is a commodity currency, influenced by the prices of Australia’s natural resources, such as iron ore and coal.
- High Interest Rates: Australia tends to have higher interest rates than other developed countries.
- Strong Economy: Australia has a strong and growing economy.
7. Singapore Dollar (SGD):
- Stable Economy: Singapore has a stable and diversified economy.
- Financial Hub: Singapore is a major financial hub in Asia.
- Strong Government: Singapore has a strong and well-managed government.
8. Special Drawing Rights (SDR):
- IMF Reserve Asset: The SDR is an international reserve asset created by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- Basket of Currencies: Its value is based on a basket of five major currencies: USD, EUR, RMB, JPY, and GBP.
- Stability: Provides diversification and stability as it is not tied to any single country.
Considerations for Choosing Alternative Currencies:
- Transaction Costs: Consider the transaction costs associated with converting to and from the alternative currency.
- Liquidity: Ensure the currency has sufficient liquidity to meet your needs.
- Volatility: Assess the volatility of the currency and its potential impact on your transactions.
- Economic and Political Stability: Evaluate the economic and political stability of the country issuing the currency.
By diversifying currency holdings and considering these alternative currencies, businesses and investors can reduce their reliance on the EUR and RMB and mitigate currency risk.
9. The Role of Digital Currencies in EUR/RMB Transactions
How can digital currencies like Bitcoin or stablecoins facilitate EUR/RMB transactions, and what are the potential benefits and risks?
Digital currencies, such as Bitcoin and stablecoins, offer potential benefits and risks in facilitating EUR/RMB transactions. These cryptocurrencies can provide alternative methods for transferring value across borders, but it’s important to understand their implications.
Potential Benefits:
- Faster Transactions: Digital currency transactions can be faster than traditional bank transfers, which often involve multiple intermediaries and can take several days.
- Lower Fees: In some cases, digital currency transactions can have lower fees compared to traditional methods, especially for cross-border transfers.
- 24/7 Availability: Digital currency networks operate 24/7, allowing for transactions at any time, regardless of bank hours.
- Decentralization: Decentralized digital currencies like Bitcoin are not controlled by any single entity, reducing the risk of censorship or interference.
- Transparency: Transactions are recorded on a public blockchain, providing a transparent and auditable record.
Bitcoin (BTC):
- Decentralized: Bitcoin is a decentralized cryptocurrency, meaning it is not controlled by any government or financial institution.
- Global Acceptance: It is accepted by a growing number of merchants and businesses worldwide.
- Volatility: Bitcoin is known for its price volatility, which can make it risky for transactions.
Stablecoins:
- Pegged to Fiat Currencies: Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value by being pegged to a fiat currency like the USD or EUR.
- Reduced Volatility: Their stability reduces the risk of price fluctuations, making them more suitable for transactions.
- Examples: Examples include Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), and Binance USD (BUSD).
Potential Risks:
- Volatility: While stablecoins aim to reduce volatility, other digital currencies like Bitcoin can be highly volatile, making them unsuitable for some transactions.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape for digital currencies is still evolving, and regulations can vary widely by country.
- Security Risks: Digital currency exchanges and wallets are vulnerable to hacking and theft.
- Scalability Issues: Some digital currency networks have scalability issues, which can lead to slow transaction times and high fees during periods of high demand.
- Counterparty Risk: Using digital currency exchanges and other intermediaries involves counterparty risk, as these entities could potentially fail or be subject to fraud.
- Tax Implications: Digital currency transactions can have complex tax implications, and it’s important to consult with a tax professional to ensure compliance.
How Digital Currencies Can Facilitate EUR/RMB Transactions:
- Conversion to Stablecoin: Convert EUR to a stablecoin like USDT or USDC.
- Transfer via Blockchain: Transfer the stablecoin to a recipient in China via a blockchain network.
- Conversion to RMB: The recipient converts the stablecoin to RMB through a digital currency exchange.
Example:
A business in Europe wants to pay a supplier in China. Instead of using a traditional bank transfer, they convert EUR to USDT, transfer the USDT to the supplier in China, and the supplier converts the USDT to RMB through a local exchange.
Considerations for Using Digital Currencies:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with all applicable regulations in both the Eurozone and China.
- Security Measures: Use secure wallets and exchanges with strong security measures.
- Volatility Management: If using volatile cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, consider hedging strategies to manage price risk.
- Transaction Fees: Compare transaction fees across different digital currency networks and exchanges.
By understanding the potential benefits and risks, businesses and investors can make informed decisions about using digital currencies to facilitate EUR/RMB transactions.
10. Future Trends in EUR/RMB Exchange and Trade
What are the anticipated future trends in EUR/RMB exchange rates and trade relations between Europe and China?
Predicting future trends in EUR/RMB exchange rates and trade relations between Europe and China involves analyzing various economic, political, and technological factors. Here are some anticipated trends:
1. Increased RMB Internationalization:
- Greater Use in Trade: The RMB is expected to play an increasingly significant role in international trade, including trade between Europe and China.
- Expansion of CIPS: China’s Cross-Border Interbank Payment System (CIPS) is likely to expand, facilitating more RMB-denominated transactions.
- Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC): The development and adoption of China’s digital yuan (e-CNY) could further promote RMB internationalization.
2. Shifting Trade Dynamics:
- Increased Trade Volume: Trade between Europe and China is expected to continue growing, driven by increasing demand for goods and services in both regions.
- Focus on High-Tech Sectors: Trade in high-tech sectors, such as electric vehicles, renewable energy, and digital technologies, is likely to increase.
- Supply Chain Diversification: European companies may seek to diversify their supply chains to reduce reliance on China, which could impact trade flows.
3. Geopolitical Influences:
- Trade Tensions: Geopolitical tensions, such as trade disputes and political disagreements, could create volatility in EUR/RMB exchange rates and disrupt trade relations.
- Strategic Partnerships: Strengthening strategic partnerships between Europe and China could foster closer economic ties and promote trade.
- Global Economic Conditions: Global economic conditions, such as recessions or periods of high growth, will continue to influence trade and exchange rates.
4. Policy Changes:
- Monetary Policy: Changes in monetary policy by the European Central Bank (ECB) and the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) will continue to impact exchange rates.
- Fiscal Policy: Government spending and taxation policies in both regions will influence economic growth and trade.
- Regulatory Reforms: Regulatory reforms, such as easing capital controls or promoting financial market liberalization, could affect currency flows and exchange rates.
5. Technological Advancements:
- Digital Currencies: The adoption of digital currencies and blockchain technology could transform cross-border payments and trade finance.
- E-Commerce: The growth of e-commerce platforms will continue to drive trade between Europe and China.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered tools could enhance trade efficiency and improve forecasting of exchange rates.
6. Exchange Rate Volatility:
- Increased Fluctuations: EUR/RMB exchange rates are expected to remain volatile, influenced by various economic and political factors.
- Risk Management: Businesses and investors will need to implement effective risk management strategies to mitigate the impact of exchange rate fluctuations.
7. Sustainability and Green Finance:
- Green Trade: Increased focus on sustainable development and green finance could drive trade in environmentally friendly products and services.
- Green Bonds: The issuance of green bonds and other sustainable financial instruments could attract investment and promote trade.
8. Investment Flows:
- Increased Investment: Investment flows between Europe and China are expected to continue growing, driven by opportunities in various sectors.
- Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): China’s Belt and Road Initiative could attract investment and promote trade with European countries.
Example Scenario:
Increased use of the RMB in trade between Europe and China, driven by the expansion of CIPS and the adoption of the digital yuan. This could lead to a gradual shift away from the USD as the primary currency for trade settlement.
By monitoring these trends and adapting their strategies accordingly, businesses and investors can navigate the evolving landscape of EUR/RMB exchange and trade relations.
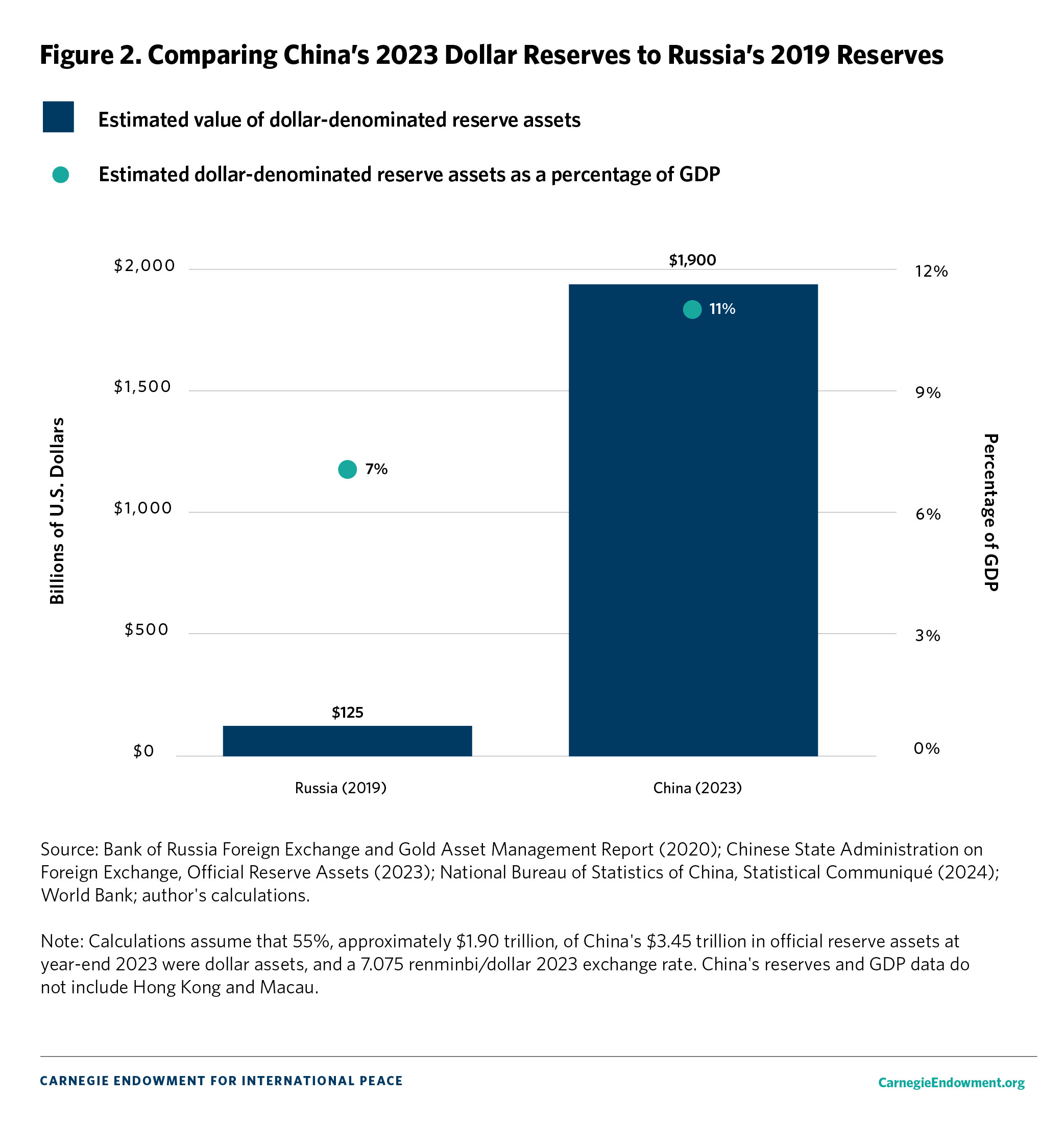 Comparing China’s 2023 Dollar Reserves to Russia’s before the Russian Central Bank’s Recent Dollar Asset Sales
Comparing China’s 2023 Dollar Reserves to Russia’s before the Russian Central Bank’s Recent Dollar Asset Sales
11. Expert Opinions on EUR/RMB Conversion
What do financial experts and economists say about the EUR/RMB exchange rate, and what are their recommendations?
Financial experts and economists offer valuable insights on the EUR/RMB exchange rate, providing guidance for businesses and investors. Here’s a summary of their opinions and recommendations:
1. Macroeconomic Factors:
- Economic Growth: Experts emphasize the importance of monitoring economic growth in both the Eurozone and China. Strong growth in either region can lead to currency appreciation.
- Inflation Rates: Economists advise keeping a close eye on inflation rates, as higher inflation can weaken a currency.
- Interest Rate Differentials: Experts highlight the impact of interest rate policies set by the European Central Bank (ECB) and the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) on capital flows and exchange rates.
2. Geopolitical Influences:
- Trade Relations: Financial analysts stress the need to watch trade relations between Europe and China. Trade disputes or agreements can create volatility in exchange rates.
- Political Stability: Experts recommend monitoring political stability in both regions, as political unrest can deter investment and weaken currencies.
3. Policy Changes:
- Monetary Policy: Economists advise staying informed about changes in monetary policy, such as quantitative easing or tightening, as these can directly impact currency values.
- Currency Controls: Experts note the influence of China’s capital controls on the RMB’s exchange rate. Policy changes regarding these controls can lead to significant currency movements.
4. Risk Management:
- Hedging Strategies: Financial experts recommend using hedging strategies, such as forward contracts and currency options, to manage exchange rate risk.
- Diversification: Economists suggest diversifying currency holdings to reduce reliance on the EUR and RMB.
5. Long-Term Trends:
- RMB Internationalization: Experts predict that the RMB will continue to play an increasingly significant role in international trade and finance.
- Shifting Trade Dynamics: Financial analysts anticipate a continued growth in trade between Europe and China, with a focus on high-tech sectors.
6. Digital Currencies:
- Potential Benefits: Some experts see potential benefits in using digital currencies like stablecoins to facilitate EUR/RMB transactions, citing faster transactions and lower fees.
- Regulatory Risks: Others caution about the regulatory risks and security concerns associated with digital currencies.
7. Expert Recommendations:
- Stay Informed: Continuously monitor exchange rates, economic news, and policy changes in both the Eurozone and China.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with financial advisors who specialize in currency risk management.
- Implement Risk Management Strategies: Use hedging strategies and diversification to mitigate the impact of exchange rate fluctuations.
- Consider Long-Term Trends: Factor in long-term trends, such as RMB internationalization and shifting trade dynamics, when making financial decisions.
- **Exercise Caution with Digital Currencies
