165 Euros in Dollars: Understanding the Impact of a Strong Dollar on Developing Countries
The recent surge in the value of the U.S. dollar has significant implications for developing economies. A strong dollar, currently equivalent to approximately 165 euros, impacts these nations in various ways, primarily through increased import costs, rising debt burdens, and hindered economic growth. This article examines the multifaceted effects of a strong dollar on developing countries.
The Dollar’s Ascent and Its Ripple Effects
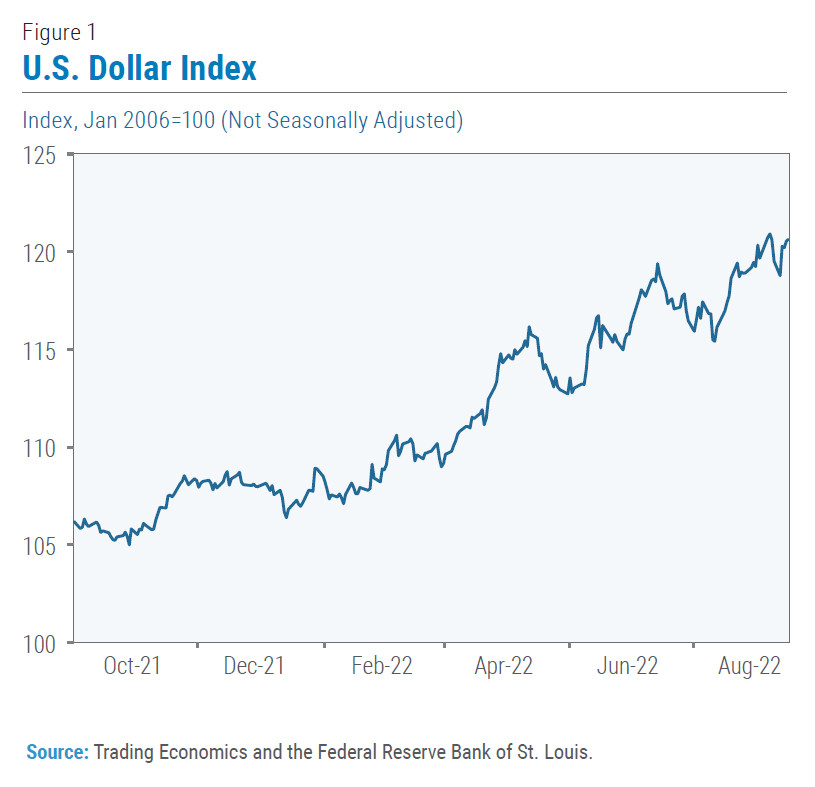
The U.S. dollar has appreciated considerably, reaching a 20-year high. This surge is largely attributed to aggressive interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve aimed at combating inflation. This has made the dollar more attractive to investors seeking stability and higher returns, leading to capital flight from developing countries.
This capital outflow weakens local currencies against the dollar. Several emerging market currencies, including the Argentine peso and the South African rand, have experienced substantial depreciation.
Debt Burden Amplified
Many developing countries hold significant external debt denominated in U.S. dollars. As their local currencies weaken, servicing this debt becomes more expensive, straining national budgets and potentially leading to debt crises.
Economic Growth Impacted
A strong dollar also makes imports, particularly essential commodities like food and energy, more costly for developing countries. This can fuel inflation, erode purchasing power, and hinder economic growth. Higher import costs, coupled with rising borrowing costs due to higher interest rates globally, stifle investment and economic activity.
Countering the Trend: The Ruble’s Resilience
While most developing countries grapple with the strong dollar, some have bucked the trend. The Russian ruble, despite initial declines, has appreciated significantly due to factors such as capital controls, export requirements, and a surge in energy prices.
A Challenging Outlook
The sustained strength of the dollar poses significant challenges for developing countries. It exacerbates existing vulnerabilities, hindering their ability to recover from the pandemic and achieve sustainable development goals. The continued appreciation of the dollar, coupled with rising global interest rates, paints a concerning picture for the economic prospects of many developing nations. The current exchange rate of approximately 165 euros to the dollar underscores the magnitude of this challenge. The international community needs to address these issues to mitigate the adverse impacts on vulnerable economies.